Basic Linux Commands
Basic Linux Commands | Linux Commands | Linux command to change directory | Linux command to create new user | Linux command to delete user | Linux command to create new folder | Linux command to view files | Linux command to delete files | Linux command to delete folder | Linux head command | Linux Tail command | Linux command to create new file | pwd command | grep command | Linux command to zip a file or folder | Linux command to unzip file or folder
Get Started:
So guys to we are going to discuss about Linux commands. So if you are a admin or a normal user and wants to work with Linux or Unix OS (operating system) you should know the basic commands to handle your daily work activities that can be maintain users or file handling. So let’s get started.
Linux Admin Commands:
Note:
- Below Commands are explaining as a Ubuntu user. Commands can be mismatched or bit differs for another Linux OS.
- Admin commands can be performs by admin or root users only.
Create User:
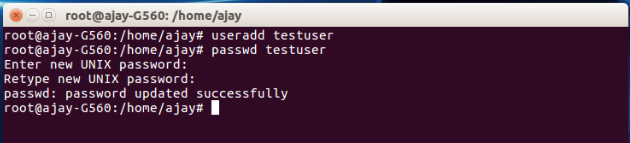
You can create a new user by given commands “adduser” or “useradd”. Here we are showing you example with command “useradd”.
First you need to switch to the root account, for that type below command to enter root account and root password:
$su - root
To create a new user gives command to your terminal as:
$useradd USERNAME
The above command will create a new user with the name of USERNAME.
To add password at USERNAME type below:
$passwd USERNAME
The above command will set password to your USERNAME
To verify you can switch to the new user account by given below command and USERNAME password:
$su – USERNAME
Check the below Screen Shot:
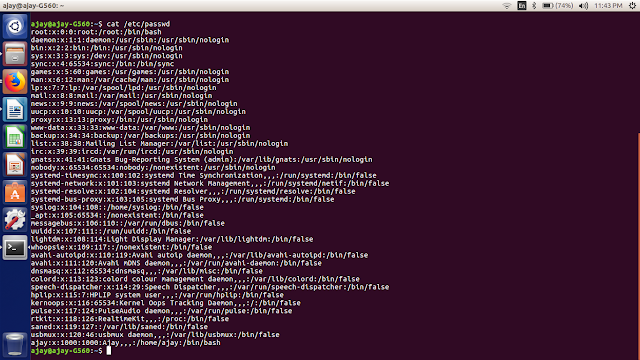
View Users:
To view the number of user in your Linux machine you need to check the below path file:
$cat /etc/passwd
Checkout below image:
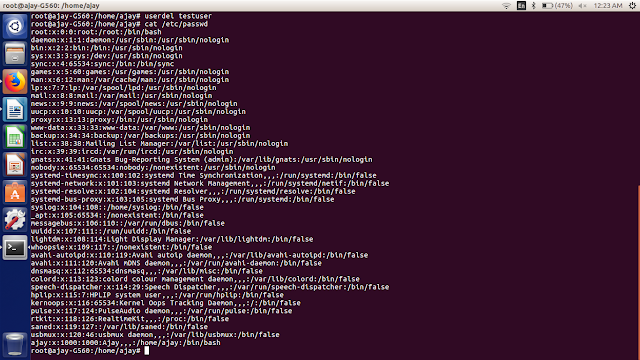
Delete User:
To delete a user you have to give command as:
$useldel USERNAME
The above command will delete the particular user.
Checkout below image:
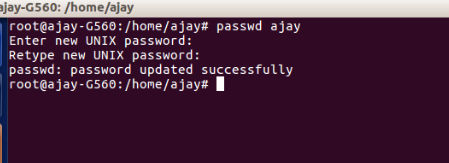
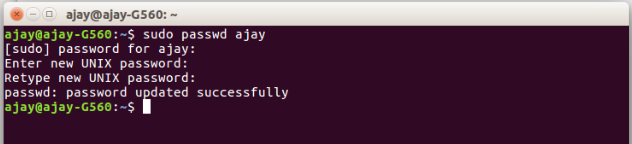
How to change User Password:
To change your password you can change them from below two methods:
$passwd USERNAME
$sudo passwd USERNAME
Working with Files and Folders:
Create a File:
To create a file you can use two ways 1st is by
using “touch” command or 2nd is by using “vi”
command by vi editor. In this post first we will create file using “touch”
command and edit it later using “vi” command.
So let’s start,
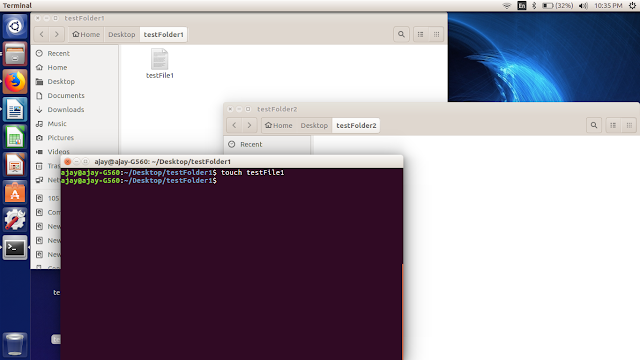
To create a file in Linux system we use below command:
$touch filename
As in below image you can see we have created “testFile1” using touch command, which is a blank file.
Edit & Save a File:
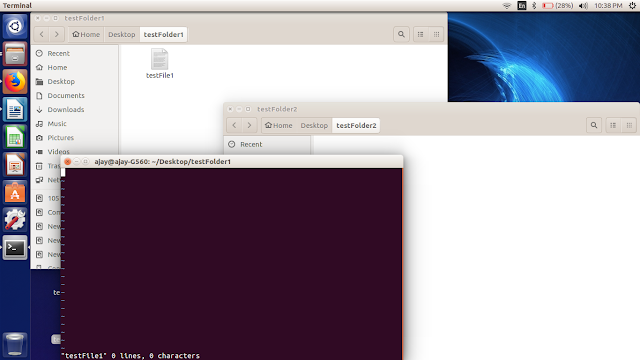
To edit a file or to add data/text into your file we use:
$vi filename
In below image we open “testFile1” to insert some dummy data into it using above command. After given your command your terminal will look like below image:
To add data into your file and to save it you need to follow below steps:
- First press “i” button from keyboard once to insert data to your file.
- Once you done with your data adding press “ESC” button from your keyboard once to get out from the editing.
- At last type “:wq” and hit “enter”.
Your file is save now.
View a File:
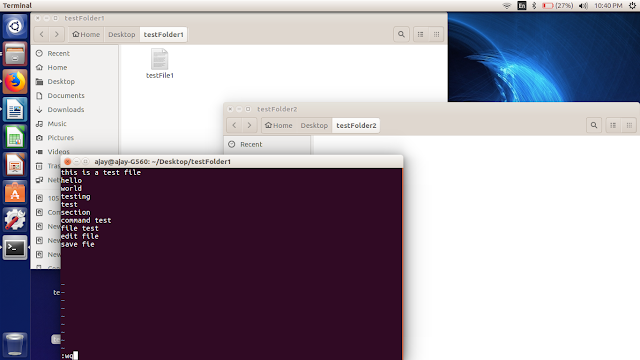
To view your saved files, go to the file path and type:
$cat fileName
In below image we can see our data which we add in previous commands.
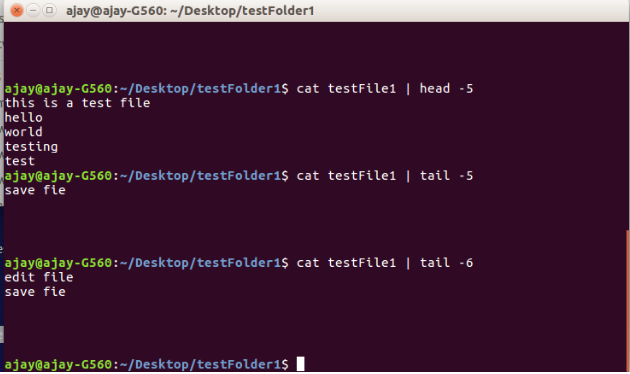
Head and Tail Command:
If you have a big list file and you wanted to see only few lines of your files from top or from bottom, “head” and “tail” commands are here, these commands are running through pipe.
To view top lines you need to give “head” command:
$cat filename | head –n
(n is number of lines you wanted to print)
To view bottom lines you need to give “tail” command:
$cat filename | tail –n
(n is number of lines you wanted to print)
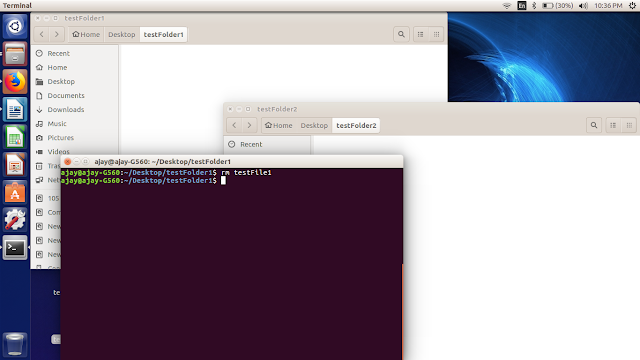
Delete a File:
To delete a file you can use below command:
$rm fileName
Create a Folder:
To create a folder use below command:
$mkdir folderName
As you can see we have created a folder with the name “testFolder1” at desktop.
Delete a Folder:
To delete a folder use below command:
$rm –rf folderName
You can see, we deleted “testFolder1”.
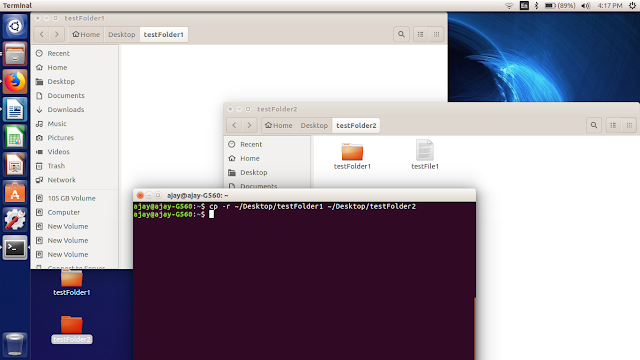
Copy File and Folder:
To copy a file we will use:
$cp “path_of_the_file” “path_of_the_location"
To copy a folder we will use:
$cp –r "path_of_source_folder" "path_of_destination_folder"
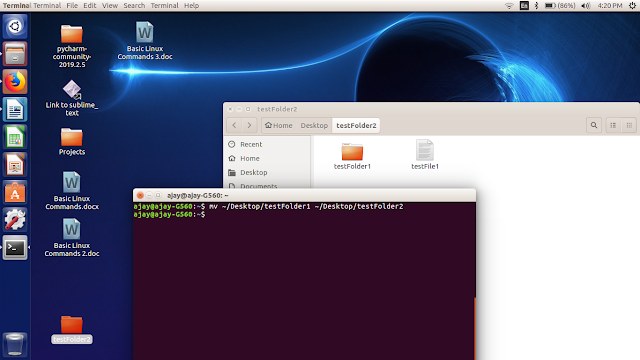
Move File and Folder:
To move a file or folder we use below command:
$mv “path_of_source_file” “path_of_destination”
To move a folder use:
$mv “path_of_source_folder” “path_of_destination”
Archive your data:
TAR or UNTAR a file:
To make a file or folder in archive in Linux we generally make them tar.
Tar is default command which is present in every Linux system. If you want to zip/rar then you need to install particular packages first in many Linux systems.
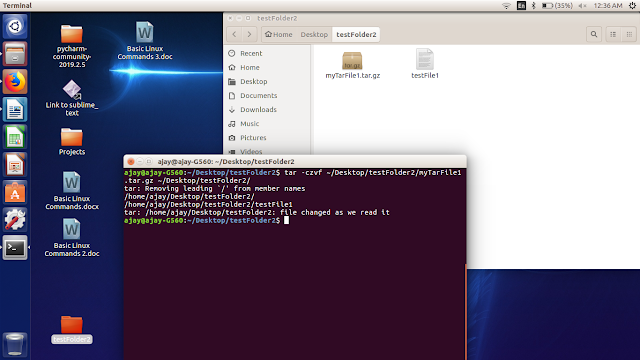
To tar a file:
$tar –czvf filename_with_extention_.tar.gz location_where_to_save
$tar –xvf filename.tar.gz
Other Important Commands:
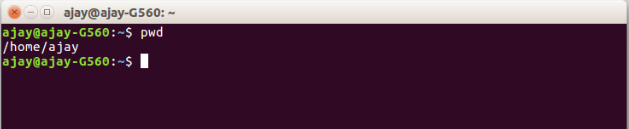
View current path:
To view the current path where user is present right now we use:
$pwd
(pwd stands for present working directory)
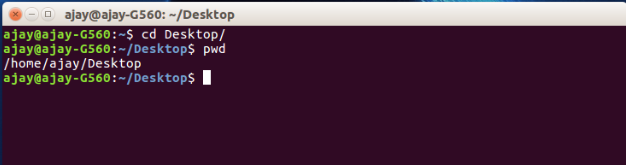
Change current path:
To change the current path we use cd command which stands for change directory.
$cd directory_path
Use of GREP:
GREP command is use to list out or find some particulate file if present.
$grep “ajay”
Use of PIPE:
The PIPE symbol is use to connect two command to perform a single output.
$ls | grep “something”
The above command will list out items and list out “something” as result if present.
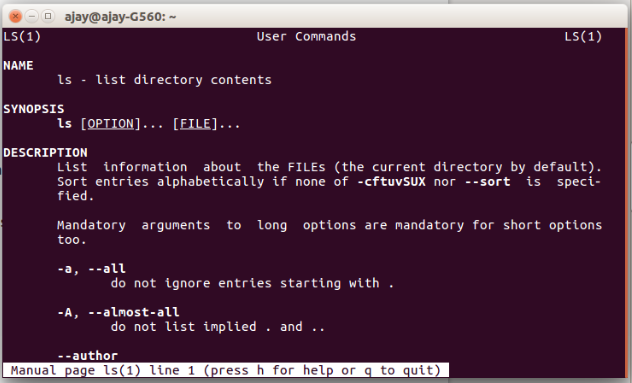
Use of MAN command:
This command is usually use to get manual of any command. You can get a deep detail of the target command. This command work like:
$man commandName
When you run the command it will look like:
$man ls
Check the active users:
To check the list of active user you can type below command:
$who
The above command will give you list of active user on network.
Check the History of commands:
to check the histroy of your typed command use below:
$history





















Unique content.
ReplyDeleteWell explained..
Very nice concept and learning that is helpful 👍
ReplyDeleteNicely explained and informative...
ReplyDelete