Variables and Operators in R Programming Language
Hello friends today we will talk about two topics:
- Variables in R programming
- Operators in R programming
Variables in R programming
A variable can store a number, an object, a string, data structures of r and so on. You need to define the name of the variable to store any value on it.
Ex:
>var1 <- 25
>var2 <- “Hello”
“Variables are containers to store a value in it.”
Note:
Before defining a variable name just be sure the points below, which are showing the right and wrong method to declare a variable:
Right Method:
- Variable can start with a dot, but dot should not be followed by a number. In this case, the variable will be invalid.
- The variable contains letter, number and underscore and starts with a letter.
- Can start with a dot(.) but the dot(.)should not be followed by a number.
Example for Right declaration:
>variable_name
>variable.name
>variable_name2
>variable23
>variable_53.
Wrong Method:
- Variable name can't start with an underscore(_).
- we can't use any special character in the variable name except dot and underscore.
- Variable name cant starts with a numeric digit.
- A variable name cannot start with a dot which is followed by a digit.
Example for Wrong declaration:
>variable_name%
>2variable_name
>.2variable_name
>_variable_name
you can check the type of variable you declared by giving the “class” method:
>var <- 25
>print(class(var))
Result: numeric
>var <- “hello”
>print(class(var))
Result:character
Hope you understood the concept for declaring a variable in R. Lets go to the next topic.
Operators in R
Operators are used to perform various kind of operations between the operands. They simulated the various mathematical, logical, and divisional operations performed on a set of Complex Numbers, Integers, and Numerical as input operands.
Well you can say that operators are very basic common feature presents in all types of programming languages. In R we have mainly five(5) types of operators:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Miscellaneous Operators
lets discuss them one by one:
Arithmetic Operators:
These operators are use to make mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, division, multiplication and so on. Check out the below arithmetic operations table:
Operators |
Description |
+ |
Addition |
- |
Subtraction |
* |
Multiplication |
/ |
Division |
^ |
Exponent(first vector raised to the exponent of second vector) |
%% |
Modules(Reminder from Division) |
%/% |
Integer Division(the result of division of first vector with second (quotient)) |
check out the below Example:
Relational Operators:
these operators are used to ind out the relation between two operands provided to them. These operators are commonly knows as “greater then, less then, equals to, greater then or equals to, less then or equals to, not equals to” and so on. Check out the below relational operators table.
Operators |
Description |
< |
Less then(is first operand is less then second operand) |
> |
Greater then |
== |
Equals to |
<= |
Less then or equals to |
>= |
Greater than or equals to |
!= |
Not equal |
check out the below example:
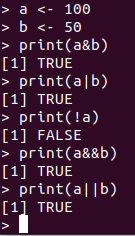
Logical Operators:
These operators in R, basically work only for the basic data types logical, numeric and complex and vectors of these basic data types.
Check out the below table:
Operators |
Description |
& |
Logical AND operation (Element Wise) |
| |
Logical OR operation (Element Wise) |
! |
Logical NOT operation (Element Wise) |
&& |
Logical AND operation (Operand Wise) |
|| |
Logical OR operation (Operand Wise) |
Check out the below example:
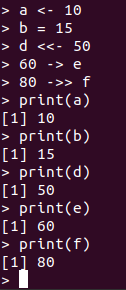
Assignment Operators:
These operators are used to assign the values to the variables. Check out the below table:
Operators |
Description |
<-, =, <<- |
Called Left Assignment |
->, ->> |
Called Right Assignment |
Check out the below example:
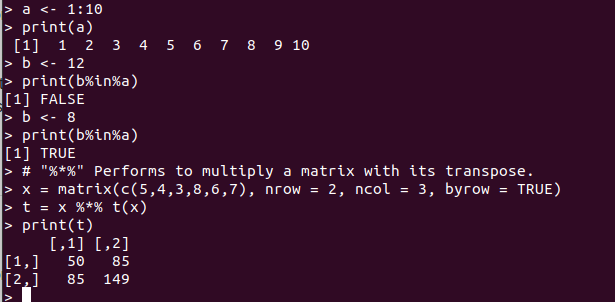
Miscellaneous Operators:
These operators are used to manipulating the data, for specific purpose and not general mathematical or logical computation. Check out the below table:
Operators |
Description |
: |
Create Series of numbers from left operands to right one. |
%in% |
Identifies if left element belongs to right one |
%*% |
Performs to multiply a matrix with its transpose. |
Check out the below example:
So hope you understood the concept of Operators and variables in R. will get back to you with new tutorials very soon.
Feel free to leave your valuable comments below.
Read Also:
- Introduction to R Programming Language
- Basic Data Types of R Language
- Start Basic Working with R Language
Thank you

















Good content.. keep sharing
ReplyDelete